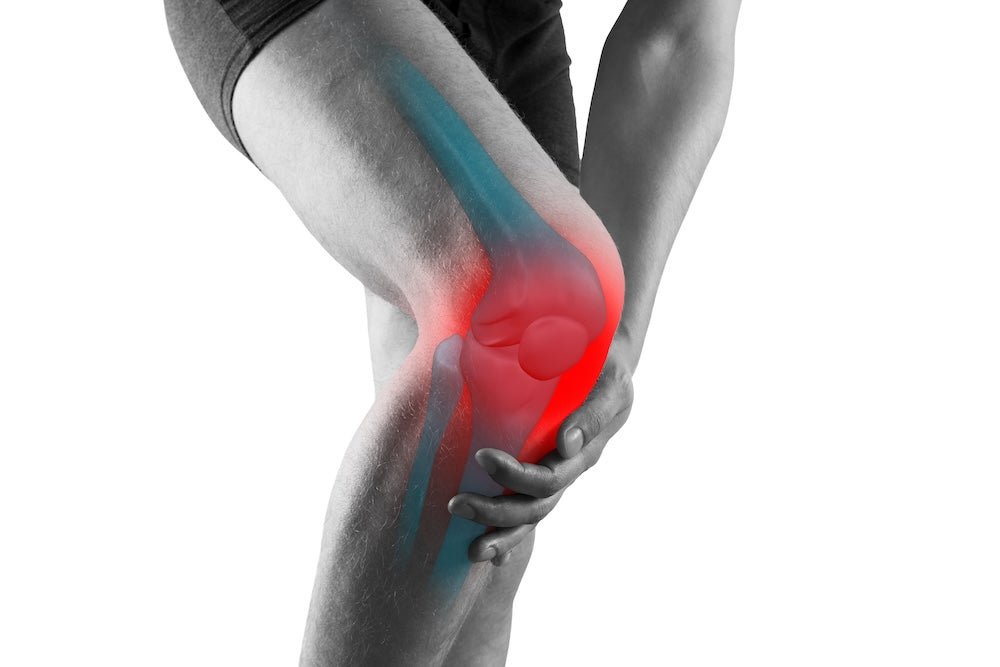
The knee joint is one of the largest and most weight-bearing joints in your body. It consists of three bones: tibia (shin bone), femur (thighbone), patella (kneecap), and a network of tendons, muscles, cartilage, and ligaments.
The two types of cartilage present in the knee are meniscus and articular cartilage, which act as shock absorbers to help the knee perform all ranges of motions without the two knee bones rubbing against each other. The two groups of muscles that build the knee joint and help your knee move are quadriceps muscles and hamstring muscles.
A problem in any part of the knee can lead to severe pain and a severe disruption in one’s quality of life. And it doesn’t just affect older adults, in fact, knee pain is one of the most common diseases affecting all age groups. In people over 65, it’s mainly due to issues associated with age, and in younger adults, the cause is either genetic disorders, knee injuries, or wear and tear due to overuse in daily activities. One of the common causes of knee pain is osteoarthritis (a type of arthritis) that mainly affects people over the age of 65 but can also affect young adults ranging from 18 to 45 years old.
Other types of knee pain include sharp knee pain, side knee pain, as well as pain due to any other knee problem or injury.
In this article, we will review sharp knee pain, its common causes, and available diagnoses and treatments.
Common Causes of Sharp Knee Pain
Sharp and stabbing pain is one of the most intense types of knee pain. It can impact either one or both knees as either mild or severe, with the intensity fluctuating depending on the severity of the condition. The problem is experienced by all people regardless of their age.
Here are some of the most common causes of sharp knee pain:
Osteoarthritis
Occurs when the knee cartilage tears, is worn out or damaged, leading to significant sharp pain while walking, standing, and climbing stairs. (Another common type of knee arthritis that can cause burning knee pain is rheumatoid arthritis).
Meniscus Tear
Meniscus acts as a cushion between the bones within the joint. Thus, wear and tear in this part of the knee is usually due to daily activities or injuries and can lead to sharp knee pain.
Ligament Injuries
Ligaments are soft tissues that stabilize the knee joint and enable all ranges of motion in the knee. Sprained ligaments not only cause sharp pain in the affected area but also lead to redness, swelling, and discomfort when moving. Some common ligament injuries include anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injuries.
Patellar Tendinitis
Also known as jumper’s knee, this is experienced when the patellar tendon is inflamed, causing sharp knee pain. It’s most commonly observed in athletes due to intense physical activity.
Knee Bursitis
The bursa is a fluid-filled sac that cushions the outside of the knee joint, protecting it from regular wear and tear, allowing tendons and ligaments to glide smoothly. Inflammation or irritation in the bursae due to repetitive stress from overuse of the joint can cause severe pain in the knee.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
The symptoms most commonly observed along with sharp knee pain are:
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Severe pain with clicking sound
- Pain while going downstairs
- Pain while standing up after sitting for a long time
- Inability to bend the knee
Diagnosing Sharp Knee Pain
Sharp knee pain is diagnosed either through a physical exam or imaging and lab tests. The physician will begin the examination by asking about your medical history and assessing the swelling and pain in the affected area. For a better understanding of the condition, a doctor may consider getting imaging done, such as:
X-rays detect any degenerative joint disease or bone fractures.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) tests are used to create 3D images inside of the knee, unfolding soft tissue-related injuries.
Computerized tomography (CT) scans, combined with X-rays, are used to create cross-sectional images of your knee joint to assess bone health and diagnose fractures–especially useful in detecting gout.
An ultrasound takes images of soft tissue within or around the knee joint from different directions using sound waves.
These imaging methods are often used together to correctly diagnose and identify the root cause of the knee problem. If healthcare specialists suspect that you have an infection or inflammation, they may also recommend blood tests to diagnose your knee problem accurately.
Treatment Options for Sharp Knee Pain
There are a number of treatment options for sharp knee pain, such as:
Non-Surgical Treatments
The RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), medications (pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications [such as ibuprofen]), and physical therapy and exercises are commonly used. However, these solutions typically only offer temporary pain relief, and you may experience discomfort after completing the therapy. For a long-lasting knee pain relief treatment, FDA-cleared Motive Knee therapy offers the best alternative approach. Motive addresses one of the main causes of knee pain, muscle weakness, by strengthening the muscles around the knee to reduce pressure on the knee joint, leading to less pain and increased mobility.
Surgical Treatments: These are prescribed by healthcare specialists when non-invasive treatment options won’t address the issue. Some severe cases of sharp knee pain can be treated by arthroscopic surgery, knee chondroplasty surgery, or knee replacement surgeries.
Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture and chiropractic care are other alternatives that ease sharp knee pain. Additionally, wearing knee braces or other support devices can help offer temporary knee pain relief.
Experience More Relief with Motive Knee
Sharp or stabbing knee pain is discomforting and affects daily activities, hindering one’s ability to live a normal life. Knee pain can affect people of all age groups and can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as swelling, redness, and stiffness with severe pain in the affected area.
Many non-surgical knee treatment approaches can treat knee pain, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, and injections. However, they only offer temporary pain relief. In such cases, Motive’s FDA-cleared therapy stands out as an effective knee pain treatment. It targets one of the root causes of knee pain, muscle weakness, by strengthening the muscles around the joint.
Motive therapy has been tested on over 20,000 people and is backed by doctors and surgeons alike. Now is the time to reclaim your life—don’t let knee pain dictate what you can and cannot do, nurture your well-being both physically and emotionally with Motive therapy. Get your Motive now!